Blog
What is Spinning in the Textile Value Chain?
Introduction
Spinning is a fundamental process in the textile value chain, serving as the bridge between raw fiber and finished fabric. It transforms natural and synthetic fibers into yarn, the essential building block for weaving, knitting, and other fabric production techniques. This crucial step significantly influences the quality, durability, and characteristics of the final textile product.
The Role of Spinning in Textiles
In the vast textile ecosystem, spinning plays the role of converting raw materials such as cotton, wool, silk, and synthetic fibers like polyester into yarn. The yarns produced are used in a variety of applications, ranging from basic apparel to advanced technical textiles.
Spinning ensures uniformity and strength in yarns, making them suitable for diverse end uses. The process directly impacts the quality of the fabric, as well-spun yarns yield better durability, appearance, and comfort.
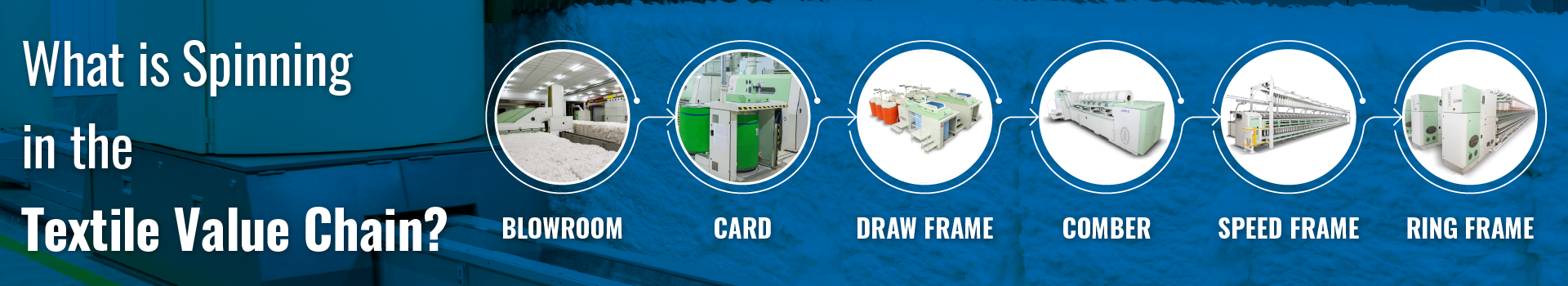
Key Steps in the Spinning Process
- Blowroom: The Blowroom process begins by opening the material into very fine tufts, preparing it for further cleaning and processing. Cleaning eliminates most impurities, such as seed particles and debris, ensuring cleaner fibers. In mixing or blending two or more types of fibers are blended to achieve a uniform and consistent mix.
- Card: Carding machines align the fibers into thin webs, separating and cleaning them further. This step individualizes the fibers and converts them into a strand called the sliver.
- Draw Frame: In the Draw Frame process, the carded sliver is further refined to enhance its uniformity. This is achieved by improving its evenness across short, medium, and long lengths. The fibers are parallelized through drafting, ensuring they align uniformly within the strand.
- Comber: The comber process focuses on enhancing the quality of the fiber by removing short fibers and any remaining impurities from the material. This step ensures that only long and consistent fibers remain, resulting in improved yarn strength and quality. The fibers are then consolidated into a highly uniform strand called a combed sliver. Starting with the comber lap as input, this process produces a combed sliver that is highly refined and ready for further stages of spinning.
- Speed Frame: The speed frame process takes the drawn sliver to achieve the desired thickness. A small amount of twist is introduced to hold the fibers together, forming what is known as roving—a pre-yarn intermediate state. The twisted roving strand is then wound onto bobbins, making it convenient for handling and transportation to the next stage. This stage transforms drawn sliver into roving, a crucial step toward creating high-quality yarn.
- Spinning: The ring frame process is where the roving is transformed into yarn. This begins with drafting, where the roving is drawn to a specific degree of fineness. The fibers are then twisted, creating a continuous and durable strand of yarn. Finally, the yarn is wound into bobbins or cones, making it ready for downstream processes such as weaving or knitting. The ring frame takes roving as input and delivers yarn as the final product.
LMW, as a pioneer in spinning technology, plays a vital role in enhancing each of these steps with innovative machinery that ensures efficiency, quality, and sustainability.
Types of Spinning Processes
- Ring Spinning: The Ring Spinning System is designed to handle a wide range of yarn counts and spin various types of fibers with ease. It produces yarn with optimal characteristics, featuring an idealized twisting mechanism that ensures higher yarn strength and superior quality.
- Rotor Spinning: Rotor spinning (or) Open-End Spinning is ideal for coarse and medium yarns handles up to Ne 40s counts. It is used in denim and industrial fabrics.
- Air-Jet Spinning: Known for its speed and ability to produce clean yarns which handles up to Ne 30s to 40s counts. This is used in viscose fiber applications.
Spinning’s Contribution to the Textile Value Chain
- Enhancing Fabric Quality: High-quality yarn is essential for producing superior fabrics. Parameters like strength and uniformity.
- Sustainability in Focus: Modern spinning technologies, such as those offered by LMW, enable the use of recycled fibers, promoting sustainability in the textile industry.
- Customization for Applications: Spinning allows customization of yarn properties to suit specific end uses, such as moisture-wicking fabrics for sportswear or high-strength yarns for industrial textiles.
The Future of Spinning: Innovations and Sustainability
As the textile industry evolves, spinning technology is becoming smarter, faster, and more sustainable. The focus on recycling and circular textile value chains is encouraging the development of spinning technologies that can handle recycled fibers effectively.
LMW’s Smart Solutions stand at the forefront of these advancements, empowering textile manufacturers to embrace sustainability while maintaining quality and productivity.
Spinning is not just a technical process; it is the heartbeat of the textile value chain. From its historical roots in hand-spun yarns to today’s high-tech spinning systems, the process continues to adapt and thrive, shaping the future of the textile industry. With LMW driving innovation, spinning remains a key driver of excellence and sustainability in textiles.






 info@lmwtmd.com
info@lmwtmd.com